How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and control navigation to advanced techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore various drone models, flight modes, and essential maintenance procedures, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
Understanding the intricacies of drone operation involves mastering both the technical aspects of the machine and the legal frameworks governing its use. This guide aims to bridge that gap, providing a comprehensive resource for both novice and intermediate pilots. We’ll cover crucial safety measures, advanced flight maneuvers, and tips for capturing stunning aerial imagery, all while emphasizing responsible and legal drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before taking flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves checking various components to ensure everything is functioning correctly and minimizing the risk of accidents or malfunctions. Neglecting this step can lead to equipment damage, injury, or legal repercussions.
Pre-Flight Inspection: A Step-by-Step Guide, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This involves visual and functional checks of critical components.
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight time. Check for any physical damage to the battery, such as swelling or cracks.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine each propeller for damage, cracks, or bends. Replace any damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Strength: Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. The number of satellites acquired should be sufficient for stable flight. A weak signal can result in erratic flight behavior.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): Verify the gimbal is functioning correctly and is properly calibrated. Test its movement to ensure smooth operation.
- Camera Check (if applicable): Check the camera lens for any obstructions or damage. Test the camera functionality to ensure it is recording properly.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts, damage, or obstructions.
- Controller Check: Ensure the controller is fully charged and properly connected to the drone. Test the controller’s responsiveness.
Pre-Flight Checklist Flowchart
The following flowchart visually represents the pre-flight checklist. This can be easily adapted for both visual and text-based representations.
[Imagine a flowchart here: Start -> Battery Check -> Propeller Check -> GPS Signal Check -> Gimbal Check (if applicable) -> Camera Check (if applicable) -> Visual Inspection -> Controller Check -> Safe to Fly? (Yes/No) -> End (Yes), Troubleshooting (No)]
Drone Model Pre-Flight Requirements Comparison
| Drone Model | Battery Check | Propeller Check | GPS Signal Strength | Other Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | Minimum 20% charge recommended | Check for cracks or damage | At least 6 satellites | Gimbal calibration |
| Autel EVO II | Minimum 15% charge recommended | Check for cracks or damage | At least 7 satellites | Sensor cleaning |
| Parrot Anafi | Minimum 25% charge recommended | Check for cracks or damage | At least 5 satellites | Camera lens cleaning |
| Skydio 2 | Minimum 30% charge recommended | Check for cracks or damage | At least 8 satellites | Obstacle avoidance system check |
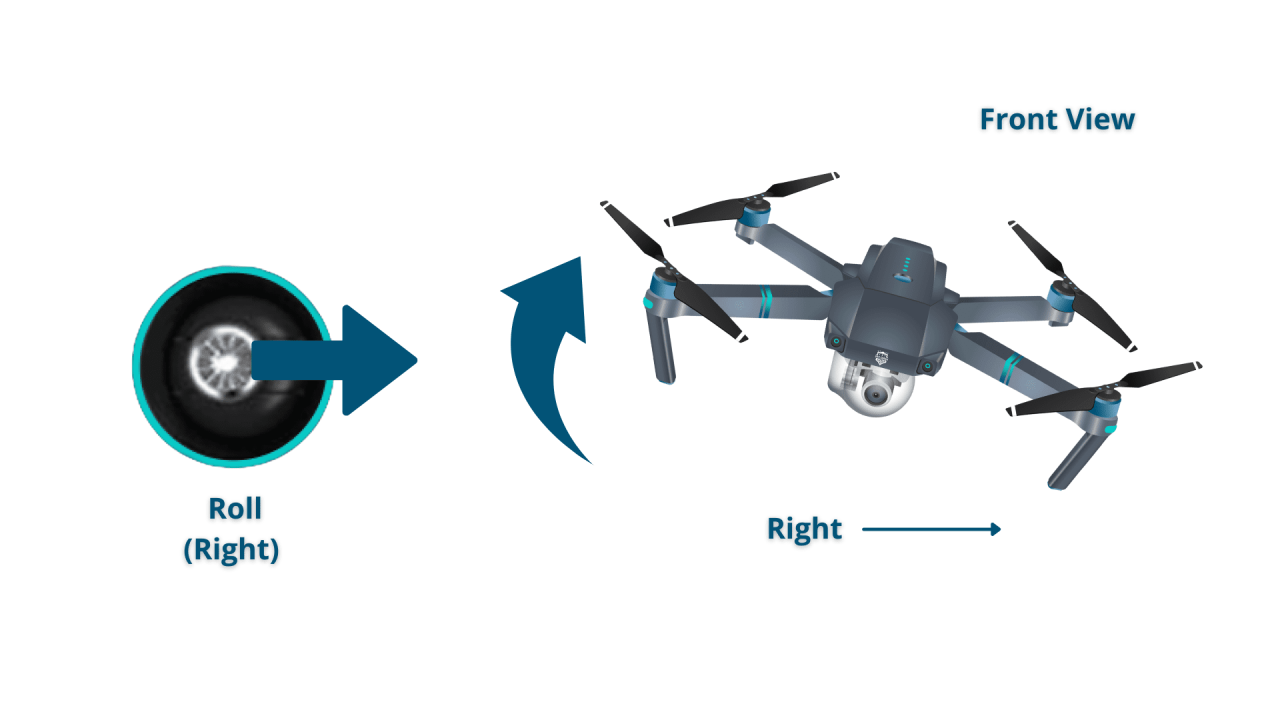
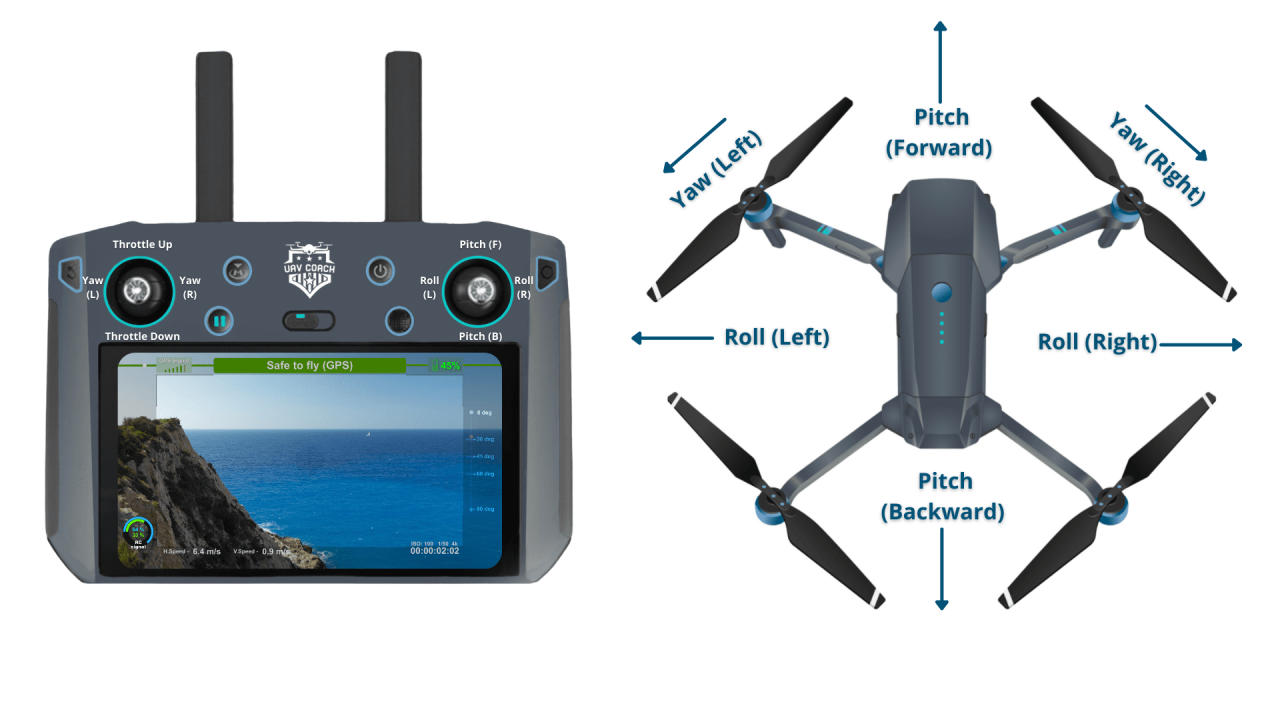
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Effective drone operation hinges on understanding and mastering the drone’s controls and various navigation modes. Different drones utilize different controllers, each with its own set of functionalities and settings.
Drone Controller Types and Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in design and features, but generally include joysticks for controlling movement, buttons for various functions (camera control, return-to-home, etc.), and possibly a screen for real-time flight data.
- Standard Controllers: These are typically handheld devices with two joysticks for controlling pitch, roll, yaw, and throttle.
- Advanced Controllers: These may incorporate additional features such as built-in screens, customizable buttons, and advanced flight modes.
- Smartphone Controllers: Some drones can be controlled via a smartphone app, offering a more accessible and intuitive interface.
Drone Navigation Systems
Drones use a variety of navigation systems to maintain position and orientation. Understanding these systems is key to safe and effective flight.
- GPS Navigation: Relies on GPS signals to maintain position and altitude. Accurate GPS is essential for stable flight and features like Return-to-Home.
- Attitude Navigation: Uses onboard sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) to maintain orientation and control, even without a strong GPS signal. Useful in GPS-denied environments but can be less stable.
- Manual Navigation: Provides direct control over the drone’s movement. Requires skill and practice.
Learning to Control a Drone: A Step-by-Step Guide
Beginners should start with basic maneuvers in a safe, open area, gradually progressing to more advanced techniques as their skills improve. Practice in a simulator before flying a real drone is recommended.
- Hovering: Practice maintaining a stable hover in a safe location.
- Basic Movements: Practice moving the drone forward, backward, left, and right.
- Altitude Control: Master controlling the drone’s altitude.
- Yaw Control: Practice rotating the drone.
- Advanced Maneuvers: Gradually introduce more complex maneuvers, such as circular flights and figure-eights.
Flight Modes and Features
Most drones offer various flight modes and advanced features to enhance control, safety, and creative possibilities. Understanding these modes and features is essential for optimizing drone performance and achieving desired results.
Drone Flight Modes
| Flight Mode | Characteristics | Recommended Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness, providing stability for beginners. | Training, initial flights |
| Sport Mode | Unlocks full speed and responsiveness. | Experienced pilots, dynamic shots |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. | Safety feature, low battery situations |
| Follow Me | Drone automatically follows a designated subject. | Filming moving subjects |
Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features add significant capabilities to drone operation, enhancing safety and creative options.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows pre-programming a flight path for automated flights.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles during flight.
- Point of Interest (POI): Allows the drone to orbit a specific point.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and post-processing workflows. High-quality results depend on optimizing both in-flight settings and post-production techniques.
Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Camera settings significantly impact image quality. Understanding and adjusting these settings is crucial for achieving professional-looking results.
- ISO: Lower ISO values generally produce cleaner images with less noise, but require more light.
- Shutter Speed: A faster shutter speed freezes motion, while a slower shutter speed can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background.
- White Balance: Ensures accurate color representation.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Effective composition is key to creating visually appealing aerial footage. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional guidelines.
Stabilizing Footage and Reducing Camera Shake
Many drones incorporate image stabilization technology to reduce camera shake. However, smooth, steady shots often require careful piloting techniques.
Post-Processing Aerial Photos and Videos

Post-processing can significantly enhance the quality of aerial photos and videos. Software like Adobe Lightroom and Premiere Pro offer powerful tools for color correction, sharpening, and other adjustments.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of your drone. Addressing common problems promptly can prevent more serious issues.
Routine Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance involves cleaning, proper storage, and careful battery care.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning to navigate effectively is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques. From there, you can practice and gradually improve your skills in operating a drone safely and efficiently.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens to remove dirt and debris.
- Storage: Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Battery Care: Store batteries at a moderate temperature and avoid fully discharging or overcharging them.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge | Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, interference, or weak signal | Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky. |
| Motor Malfunctions | Motor damage, loose connections | Inspect the motors and replace any damaged parts. |
| Gimbal Malfunction | Calibration issues, physical damage | Recalibrate the gimbal or replace damaged components. |
Recommended Tools and Supplies for Drone Maintenance
A basic toolkit for drone maintenance includes screwdrivers, cleaning cloths, and a battery charger.
Legal and Safety Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to local laws and regulations. Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues and ensure safety.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and regulations regarding airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and permitted flight areas.
Safe Operating Practices
Safe drone operation involves several key practices to minimize risks.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Drone Accident Procedures
In case of a drone accident, immediately assess the situation, secure the area, and report the incident to the relevant authorities.
Essential Safety Guidelines
- Always check weather conditions before flying.
- Never fly in strong winds or adverse weather.
- Regularly inspect your drone for any damage or malfunctions.
- Keep your drone’s firmware updated.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operation, exploring advanced techniques can unlock new creative possibilities and enhance your piloting skills.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers

Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, require practice and skill. These should only be attempted in safe, open areas away from obstacles.
FPV (First-Person View) Goggles
FPV goggles provide an immersive flying experience, enhancing situational awareness and control.
Flying in Challenging Conditions
Flying in wind or rain requires additional skill and caution. Understanding how wind affects drone flight is crucial for safe operation.
Extending Drone Flight Time
Optimizing battery performance and piloting techniques can significantly extend flight time.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation requires practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations.
Creative Aerial Photography and Videography Techniques
Experiment with different camera angles, lighting conditions, and editing techniques to create compelling aerial visuals.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical knowledge, practical skill, and a strong commitment to safety. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the process, from pre-flight preparations to advanced flight techniques. By consistently practicing safe operating procedures and staying updated on relevant regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring responsible and enjoyable flight experiences.
Remember, the skies are the limit, but safe and legal operation is paramount.
FAQs: How To Operate A Drone
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and beginner-friendly flight modes. Research reviews to find one that suits your budget and needs.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, weather conditions, and flight style. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes of flight time on a single charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If GPS signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always maintain visual contact and be prepared to take manual control if necessary.
Where can I fly my drone legally?
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority (e.g., FAA in the US) to understand airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and other legal limitations before flying.